Town Councils are autonomous legal entities formed under the Town Councils Act. A Town Council is led by elected Members of Parliament (MPs) from which the Chairperson is appointed. The Town Councils are responsible for the day-to-day operations in managing the common property of HDB residential flats and commercial property within the town.
Town Councils run the estates together with their residents within the broad legislative framework under the Town Councils Act and its subsidiary legislation (e.g. Town Councils Financial Rules). Please find more details on the Town Councils Act and its subsidiary legislation
here.
Vision and Milestones
Town Councils were formed in 1989 under the Town Councils Act to empower elected MPs and residents to work together in the management of their estates. Under this set-up, elected MPs are given the authority and responsibility to manage the public housing estates in their constituencies, with residents participating in the decision-making process. In this way, each town can develop its own distinctive character and identity.
The concept of Town Councils was first piloted in Ang Mo Kio Town and subsequently introduced island wide over three phases, from mid-1989 to mid-1991. Currently, there are 19 Town Councils managing the common property in HDB housing estates in Singapore.
1988 – 1991
Formation of Town Councils
The Town Councils Act was enacted on 5 August 1988 to empower Town Councils to take over the management and maintenance of the common property at public housing estates from HDB. The first three Town Councils were Ang Mo Kio South, Ang Mo Kio West and Cheng San Town Councils. By 1991, the management and maintenance of the common property of all HDB housing estates had been handed over to Town Councils. Legislative amendments have made to the Town Councils Act over the years to facilitate Town Councils’ operations and to enable them to operate more effectively and efficiently.
| 1992 - 2016 | Between 1992 and 2005, legislative amendments made to the Town Councils Act to facilitate Town Councils in their operations and to enable them to operate more effectively and efficiently. Town Councils were reconstituted after each General Election. |
| 2017 - Current | The Town Councils Act was amended in 2017 to improve the Town Councils’ governance and accountability, strengthen their financial management and to also enhance MND’s regulatory oversight over Town Councils. Currently, there are 19 Town Councils managing the common property in HDB housing estates in Singapore. |
Functions of Town Councils
Town Councils manage, maintain and improve the common property of the residential and commercial properties within its town for the benefit of the residents and keep them in a state of good and serviceable condition.
Common property includes facilities in the housing estates built for common use by residents, such as linkways, gardens, lifts, corridors and void decks.
Examples of key works undertaken by Town Councils are:
Routine Repairs, Servicing and Maintenance
- Building maintenance such as minor repairs to buildings e.g. plastering
- Maintenance of mechanical and electrical services such as lifts, pumps and lightings
- Periodic servicing and testing such as lift servicing, sterilising of water tanks and testing of water samples
- Essential maintenance works such as maintenance works in response to lift malfunction and failure of electricity or water supply
Landscaping and Horticulture, Conservancy and Cleaning Works
- Horticulture maintenance such as grass cutting, pruning and landscaping works
- Cleaning works to maintain estate hygiene such as sweeping and washing of common areas
- Conservancy services such as refuse collection and pest control services
Town Improvement and Upgrading Works
- Provision of facilities and amenities in the estates such as facilities for barrier-free access, community gardens, fitness corners/playgrounds, covered linkways, precinct pavilions and sheltered drop-off points
- Upkeep and upgrading of facilities and amenities in the estates
Cyclical Works
- Cyclical repairs and redecorations and repainting of buildings
- Re-roofing, electrical re-wiring, replacement of water tanks and pumps
- Replacement of lifts and their components
Town Councils are also responsible for the financial management of their towns. Town Councils are required to keep proper accounts and records of their transactions and to ensure proper financial control over their payments, expenditure and assets. Town Councils also need to ensure that they have sufficient funds for the operations of the Town Council.
Typical Organisational Structure
The typical organisation structure of a Town Council is as shown below. Town Councils can vary their structure according to their individual needs.
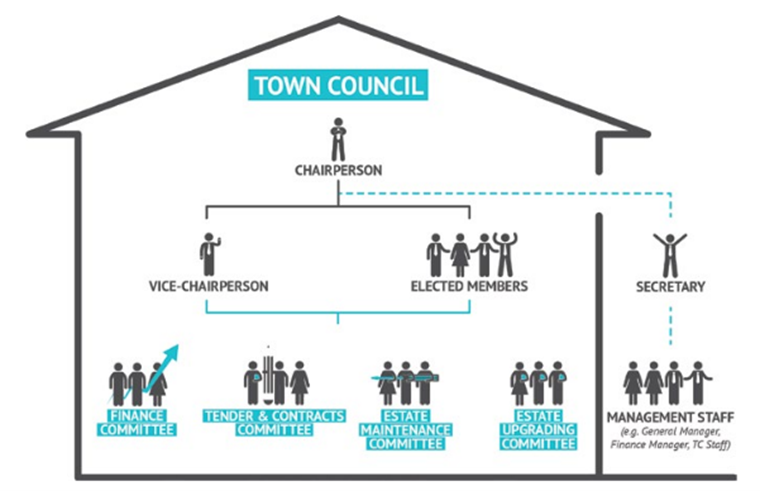
The Town Councils may appoint managing agents to manage their towns, or adopt a self-management model (i.e. hire their own employees) or a combination of both. Managing agents are service providers appointed by the Town Councils to provide expertise, resources and manpower to carry out the day-to-day operations of the Town Councils, including the supervision of other contractors and service providers.
Details of Town Councils
Currently, there are 19 Towns in Singapore comprising of 18 Group Representation Constituencies (GRCs) and 15 Single Member Constituencies (SMCs). Each Town is managed by one Town Council. The scope of each Town Council differs in terms of the resident profile, property profile (e.g. age and design of blocks managed) and number of properties in each Town.
| Town Council | Constituency |
| Aljunied-Hougang | Aljunied GRC
Hougang SMC |
| Ang Mo Kio | Ang Mo Kio GRC
Kebun Baru SMC
Yio Chu Kang SMC |
| Bishan-Toa Payoh | Bishan-Toa Payoh GRC
Marymount SMC |
| Chua Chu Kang | Chua Chu Kang GRC
Bukit Gombak SMC |
| East Coast | East Coast GRC |
| Holland-Bukit Panjang | Holland-Bukit Timah GRC
Bukit Panjang SMC |
| Jalan Besar | Jalan Besar GRC
Potong Pasir SMC |
| Jalan Kayu | Jalan Kayu SMC |
| Jurong-Clementi-Bukit Batok | Jurong East-Bukit Batok GRC
Jurong Central SMC |
| Marine Parade-Braddell Heights | Marine Parade-Braddell Heights GRC
Mountbatten SMC |
| Marsiling-Yew Tee | Marsiling-Yew Tee GRC |
| Nee Soon | Nee Soon GRC |
| Pasir Ris-Changi | Pasir Ris-Changi GRC |
| Punggol | Punggol GRC |
| Sembawang | Sembawang GRC
Sembawang West SMC |
| Sengkang | Sengkang GRC |
| Tampines | Tampines GRC
Tampines Changkat SMC |
| Tanjong Pagar | Tanjong Pagar GRC
Queenstown SMC
Radin Mas SMC |
| West Coast-Jurong West | West Coast-Jurong West GRC
Pioneer SMC |
You may visit the websites of each Town Council below for more information on the respective Town Councils.
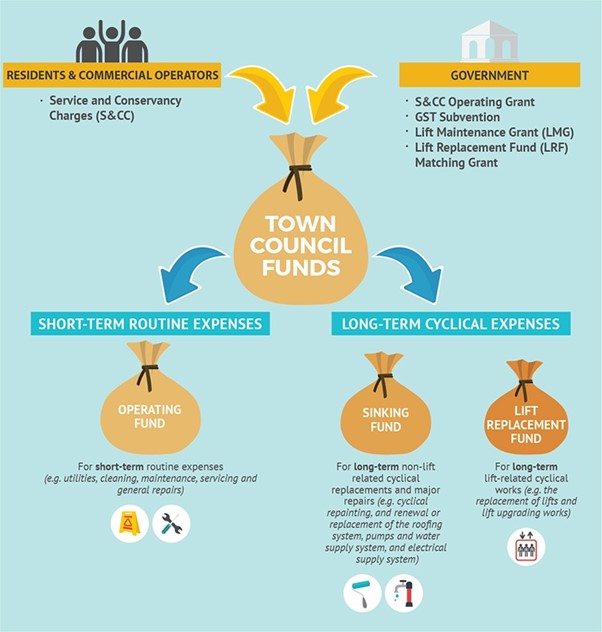
Town Council Funds
Town Councils are primarily funded by the service and conservancy charges (S&CC) collected from the residents and commercial operators within their Towns. Each Town Council sets the S&CC rates for its Town. The Government also provides grants to the Town Councils to help them with the costs of estate maintenance and to reduce residents’ cost burden. The grants include:
- S&CC Operating Grant – helps Town Councils meet their operating needs. The S&CC Operating Grant is disbursed annually for 4-room and smaller flats, with higher grants given for the smaller flat types ($33.70 per month for 1-room, $26.20 per month for 2-room, $17.00 per month for 3-room and $9.00 per month for 4-room);
- Goods & Services Tax (GST) Subvention – helps Town Councils offset the increase in GST on S&CC for HDB households. GST subvention is disbursed every quarter;
- Lift Maintenance Grant (LMG) – helps Town Councils cope with lift-related servicing and maintenance costs. The LMG is disbursed annually, at $600 for each lift maintained by the Town Council; and
- Lift Replacement Fund (LRF) Matching Grant – assists Town Councils in building up their LRF, to fund the replacement of their existing lifts. The LRF matching grant is disbursed every quarter, to match 50% of a Town Council’s quarterly contributions to its LRF.
Town Councils are required to establish and maintain separate funds for residential and commercial property, as follows:
- Operating Fund – for routine expenses, such as utilities, cleaning, maintenance, servicing and general repairs;
- Sinking Fund – for cyclical and major repairs and replacement works, such as cyclical repainting, and renewal or replacement of the roofing system, water tank, pumps and water supply system, electrical supply system, and lightning protection system; and
- Lift Replacement Fund – for the replacement of lifts and lift parts (e.g. hoisting ropes/sheaves and lift batteries), and lift upgrading works.
This illustration summarises the Town Councils’ sources of funding and how the Town Councils maintain their funds.